Blepharitis
What Is Blepharitis?
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammation of the eyelids, particularly affecting the area where the eyelashes grow. It a prevalent condition that can cause discomfort and may be associated with other eye issues like dry eye syndrome and meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD).
Types of Blepharitis
1. Anterior Blepharitis: Affects the outer front edge of the eyelid where eyelashes are attached.
2. Posterior Blepharitis: Involves the inner edge of the eyelid that comes into contact with the eyeball, often linked to MGD.
Many individuals experience a combination of both types.
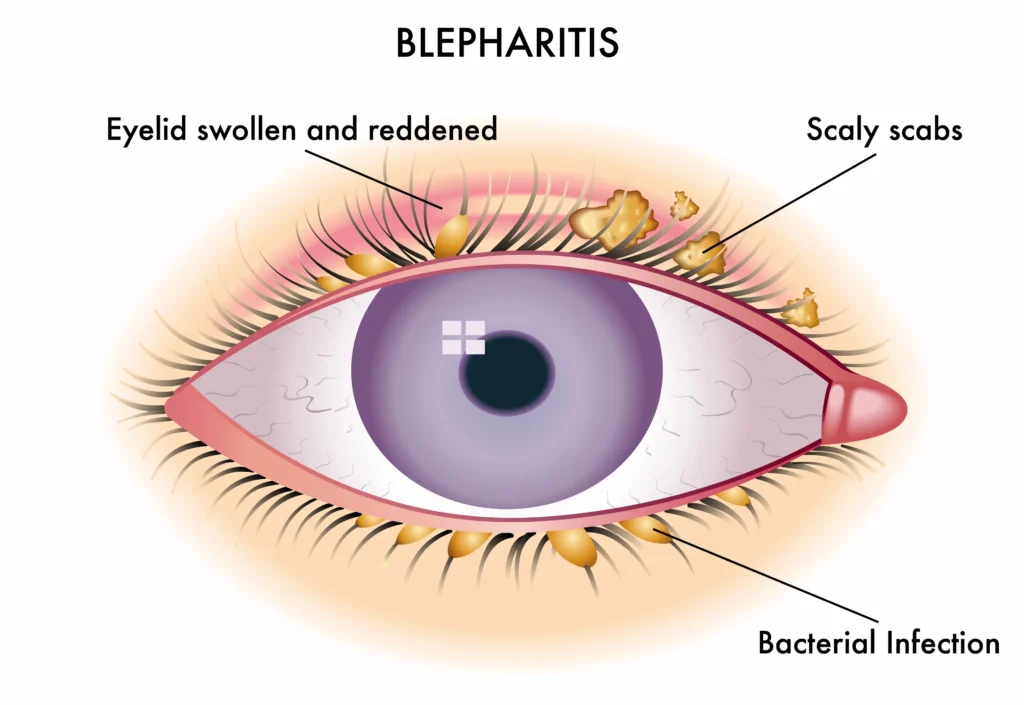
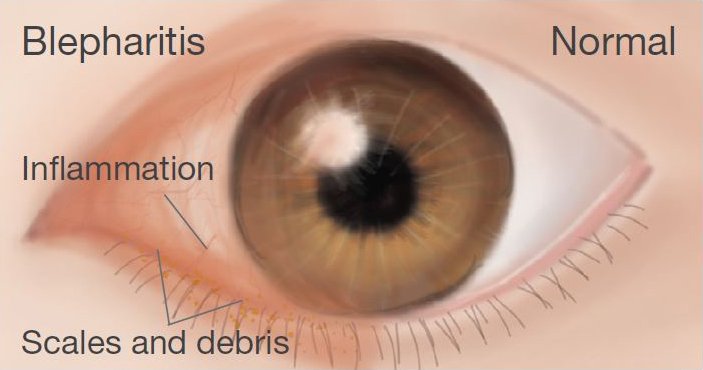
Causes
Symptoms
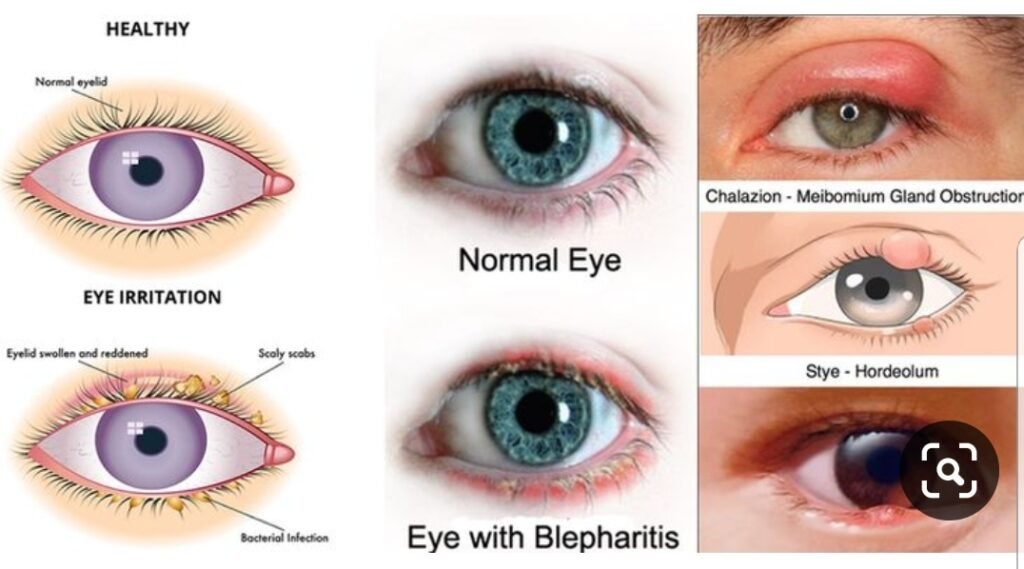

Diagnosis
An eye care professional will:
● Examine the Eyelids and Eyelashes: Using magnification to look for signs of
inflammation, crusting, or mites.
● Assess Tear Production: To determine if dry eye is present.
● Evaluate Meibomian Gland Function: To check for blockages or dysfunction.
In some cases, additional tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
While blepharitis is often a chronic condition, symptoms can be managed effectively with proper care:
1. Eyelid Hygiene
● Warm Compresses: Apply a warm, moist cloth to closed eyelids for 5–10 minutes to loosen crusts and unclog oil glands.
● Lid Scrubs: Gently clean the eyelid margins using diluted baby shampoo or over-the-counter eyelid cleansers
● Lid Massage: After warm compresses, gently massage the eyelids to express oil from the meibomian glands.
2. Medications
● Antibiotic Ointments or Drops: Prescribed to reduce bacterial infection.
● Steroid Eye Drops: Used short-term to decrease inflammation.
● Oral Antibiotics: For more severe or persistent cases, particularly when associated with rosacea.
It’s essential to use medications as directed by an eye care professional.
3. In-Office Treatments
● BlephEx: A procedure that uses a specialized device to exfoliate the eyelid margins,removing debris and bacteria.
● Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy: Targets inflammation and improves meibomian gland function, especially beneficial for patients with ocular rosacea.
4. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Potential Complications
If left untreated, blepharitis can lead to:
● Chronic Discomfort: Persistent irritation and redness.
● Eyelash Problems: Loss or misdirection of eyelashes.
● Skin Scarring: Around the eyelids.
● Secondary Infections: Such as styes or chalazia.
● Conjunctivitis: Inflammation of the eye’s surface.
● Corneal Damage: Due to prolonged inflammation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Consult an eye care professional if you experience:
● Persistent redness or swelling of the eyelids
● Painful or tender eyelids
● Vision changes
● Frequent styes or chalazia
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
References:
● Blepharitis | Johns Hopkins Medicine
● Blepharitis: What’s Behind Your Red, Itchy Eyes | UHealth Collective
● Ocular Surface Disease | Bascom Palmer Eye Institute